Intro: Iron overload (IO) reflected by elevated serum ferritins is associated with increased mortality in patients with myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) with a threshold effect seen above 1000 ug/ml (Malcovati, JCO 2005). Ferritin is elevated due to transfusions, inflammation and ineffective erythropoiesis but is an imperfect metric of true iron overload. Elevated levels of oxidatively damaging non-transferrin bound iron (NTBI) and labile plasma iron (LBI) are not easily measured but correlate with transferrin saturation (TSAT) >70% and >80% respectively (de Swart, Haematological 2018). The relationship of TSAT with ferritin and MDS-related clinical outcomes has not been well-characterized.
Objectives: We aimed to describe temporal trends in TSAT according to transfusion dependence and to determine if elevated TSAT correlates with ferritin levels, and/or predicts for clinical outcomes such as survival, infectious death and cardiac death in patients with MDS.
Methods: Adult patients enrolled in the Canadian national MDS registry over 11.5 years and 15 centers were evaluated retrospectively. Mean, median and ranges for ferritin and TSAT were calculated at six (+/- 3) month intervals. General linear mixed model analysis with repeated measures per subject was used to evaluate changes in ferritin and TSAT over time. Transfusion density (TD) was calculated at landmark year 1 and 2 and was defined as the total number of units transfused/months elapsed since commencing transfusion dependence, with TD-low and TD-high defined as above or below median. Log-rank tests were used to detect survival differences among three transfusion groups (transfusion independent [TI], TD-low and TD-high), among three TSAT groups (TSAT <50%, 50-80% and >80% at enrolment), and among three ferritin groups (≤500ug/mL, 501-1000ug/mL and >1000ug/mL at enrolment).
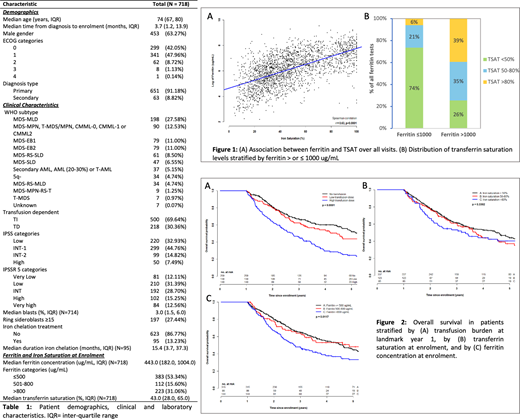
Results: A total of 718 patients from the MDS-CAN registry were included in the analysis. Patient characteristics including demographics, clinical and laboratory characteristics are summarized in Table 1. With a median follow up of 2.1 years, actuarial OS was 2.4 years. 17% developed AML and 61% of patients have died. AML, progressive disease, infection, cardiac causes, bleeding accounted for 26%, 20%, 19%, 9.6% and 6.34% of known causes of death respectively. 56% experienced infections (median 2/patient), 7% experienced a cardiac event and 43% were hospitalized at least once. Ferritin and TSAT were moderately correlated over time (r=0.63, p < 0.0001) (Figure 1A) with only 39% of all ferritins >1000ug/mL associating with a TSAT of >80%. The relationship between the 2337 serum ferritins (recorded over 42 months) and TSAT is shown in Figure 1B. Among all patients, ferritin significantly increased from enrolment up to 42 months (p<0.0001), however TSAT remained stable over time (p=0.094). There was a small but significant increase in TSAT over time only in TD patients at enrolment (p=0.0148). Transfusion dependence remained stable over time, with a median of 2.7 and 2.3 units transfused/month by landmark years 1 and 2. 5-year OS was 52% (95%CI 45-60%), 44% (95%CI 35-55%) and 25% (95%CI 18-34%) among TI patients, low-TD patients, and high-TD patients, respectively (Figure 2A). 5-year leukemia-free survival (LFS) rates among these three groups were 85% (95%CI 79-90%), 78% (95%CI 70-86%) and 73% (95%CI 62-85%), respectively with no major differences between TD-low and TD-high. Transfusion dependence (ever vs. never TD) was significantly associated with infectious deaths (p=0.0411) but not with cumulative cardiac events (p=0.4726) regardless of iron chelation status. TSAT category was not significantly associated with 5-year OS (Figure 2B), LFS, PFS or cardiac events. Conversely, ferritin category was significantly associated with 5-year OS (Figure 2C) and PFS, but not with LFS or cardiac events.
Conclusion: Among a cohort of predominantly low-intermediate risk MDS patients, TSAT correlated only moderately with serum ferritins. TD patients, and in particular high transfusion-burden TD patients have inferior clinical outcomes compared to TI or low-transfusion burden TD patients. Further analyses to probe these relationships are ongoing including the effect of TSAT and iron chelation therapy on infectious deaths, and a multivariate analysis adjusting for other covariates.
Geddes:Alexion: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Novartis: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Takeda: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Celgene: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding. Keating:Celgene: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Seattle Genetics: Consultancy; Sanofi: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Merck: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Janssen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Hoffman La Roche: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Takeda: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Taiho: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Servier: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Shire: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Leber:Otsuka Pharmaceutical: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Pfizer: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Abbvie: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; BMS/Celgene: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Amgen: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Treadwell: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Takeda/Palladin: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Alexion: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Lundbeck: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Janssen: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Shamy:Celgene: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Novartis: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding. Storring:Celgene: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Novartis: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding. Nevill:Alexion: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Celgene: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Novartis: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Honoraria. Delage:Novartis: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Celgene: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding. Elemary:Celgene: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Novartis: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding. Chodirker:Hoffman Laroche: Honoraria. Leitch:AbbVie: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Alexion: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; BMS: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Celgene: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Janssen: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Novartis: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Taiho: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Exjade: Speakers Bureau. Buckstein:Astex: Honoraria; Celgene: Honoraria; Takeda: Research Funding; Celgene: Research Funding; Novartis: Honoraria.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal